Graphics processing units (GPUs) are designed in a way that their performance can be scaled up or down during the design phase, or even after tape-out. AMD’s 9000-series, built on RDNA 4 (also known as Navi 4), is no exception. AMD confirmed this during one of its Hot Chips 2025 presentations, and demonstrated how it can cut down the design of its GPUs to produce more SKUs.
Building a product family using two GPU designs
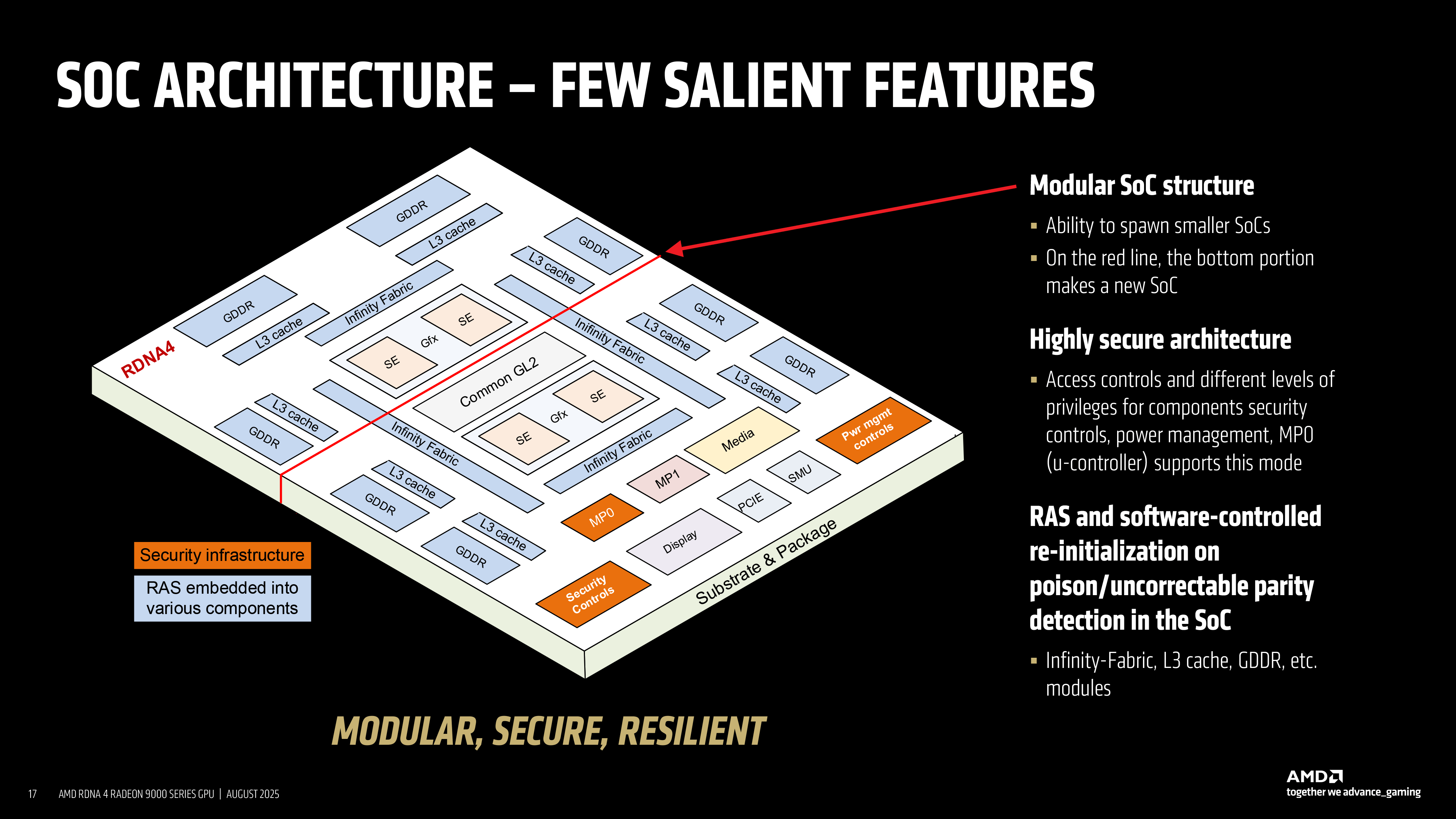
Asymmetric harvesting
The most important element of this strategy is the way a Shader Engine (SE) can be harvested. An SE is a fundamental building block of the GPU, housing multiple Work Group Processors (WGPs), Compute Units (CUs), and fixed-function stages for geometry, rasterization, and rendering. On RDNA 4-based products, AMD allows entire shader engines to be disabled when defects are present or when a lower performance target is desired. In addition to this, AMD may disable specific WGPs, which provides a lot of additional flexibility.
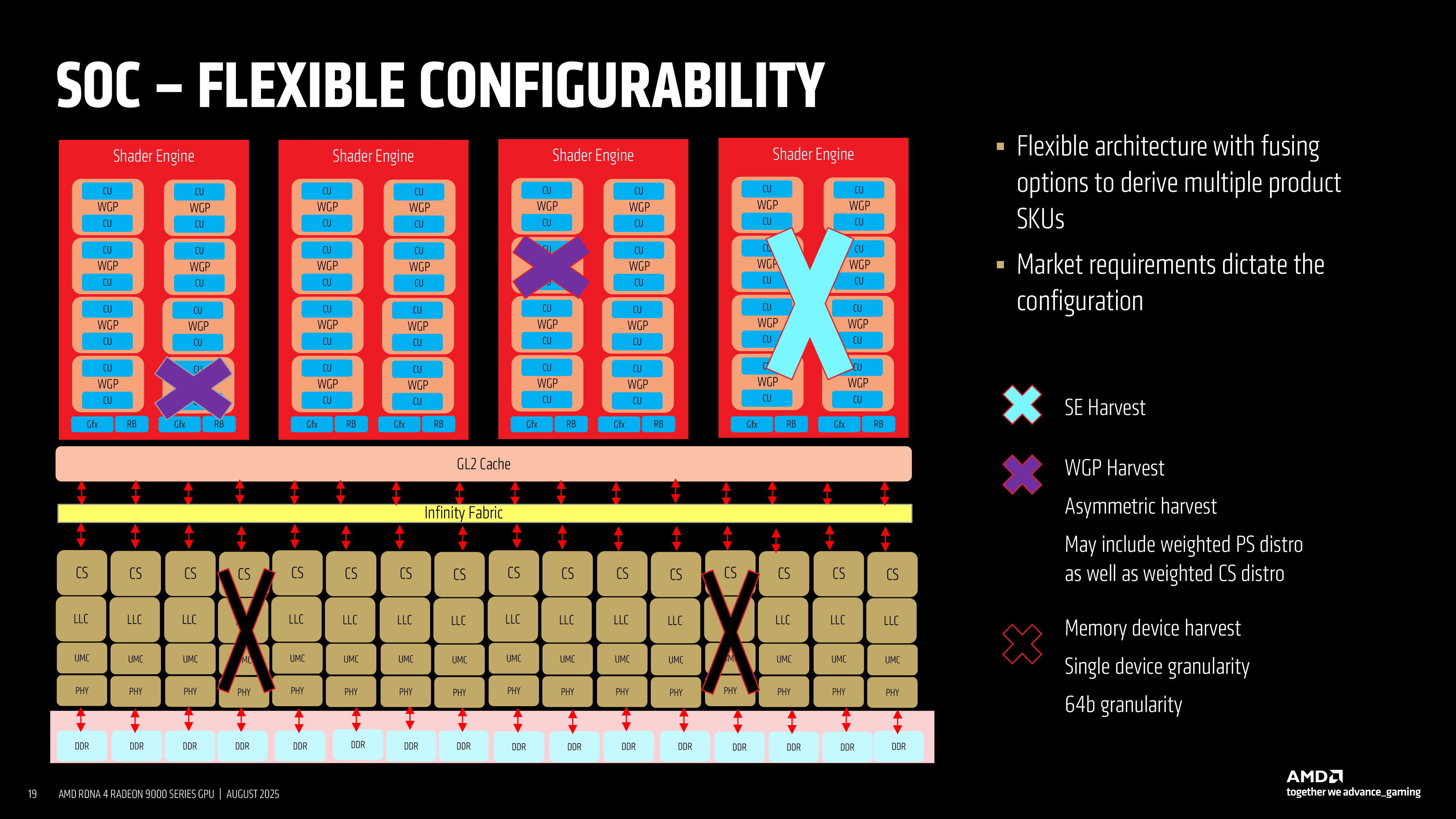
Memory harvesting adds another dimension of flexibility. The RDNA 4 memory subsystem contains multiple GDDR6 controllers, linked through Infinity Fabric and cache structures. Each memory controller can be fused off individually, meaning that AMD can reduce the effective bus width in increments of 64 bits.
For instance, a flagship model such as the Radeon RX 9070 XT includes all four shader engines, each featuring 64 compute units (with 4096 stream processors that contain ALUs), and four 64-bit memory interfaces. Meanwhile, the lower-end Radeon 9700 GRE features only three SEs, resulting in 48 CUs and 3072 SPs, and three 64-bit memory arrays, resulting in a 192-bit memory interface.
In addition to whole shader engines, smaller harvesting steps are possible through the selective disabling of work group processors inside a shader engine. This fine control enables AMD to produce products with unusual compute unit counts, such as the 56 CU Radeon RX 9070. Using this method, the Radeon RX 9070 uses a certain number of CUs instead of the whole SE. But it also comes with all memory interfaces enabled, so the RX 9070 has a full-blown 256-bit memory bus.
The concept of asymmetric harvest extends further by enabling different ratios of compute to pixel resources, ensuring that products can be tailored to gaming workloads, multimedia tasks, or compute-centric usage without redesigning the core architecture or die.
For example, the Radeon RX 9070 XT maintains a full 256-bit interface with sixteen gigabytes of memory, while the RX 9070 GRE drops to 192-bit with twelve gigabytes. Mid-range models such as the RX 9060 variants shrink further to 128-bit buses, supporting either sixteen gigabytes or eight gigabytes, depending on the SKU. This granularity allows AMD to respond to memory pricing, availability, and positioning across markets while using the same baseline silicon.
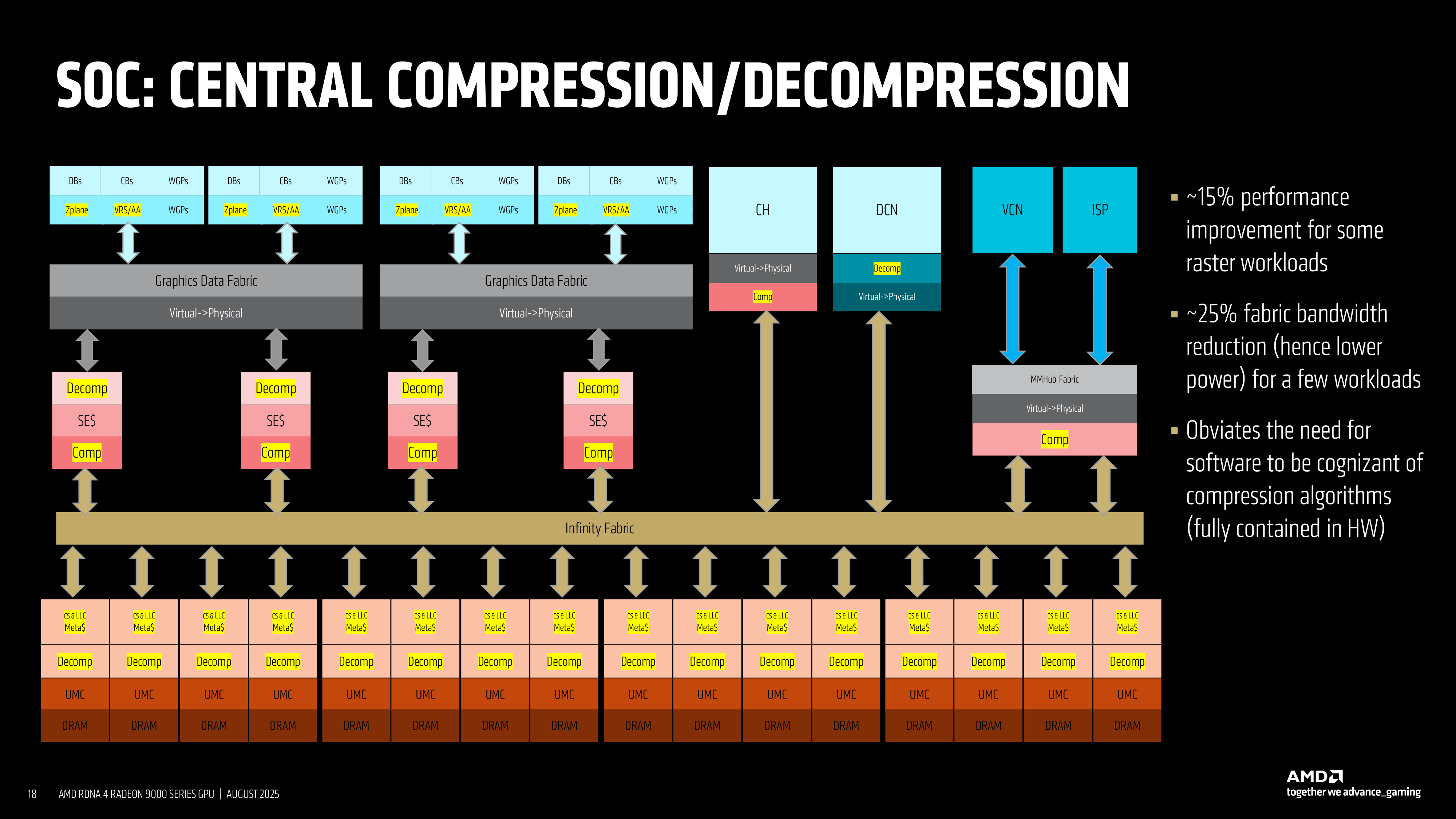
At the SoC level, RDNA 4 integrates global L2 cache blocks, compression and decompression hardware, and Infinity Fabric links (operating at 1.5 GHz – 2.50 GHz depending on the load) in a modular fashion. Because these components can handle variable data flows regardless of how many SEs or memory channels remain active, the architecture sustains efficiency, even in harvested configurations.
Centralized compression saves bandwidth and power across workloads, with AMD reporting up to a 25% reduction in fabric traffic, and a claimed 15% uplift in certain rasterization scenarios. This design ensures that whether a die is partially disabled or fully enabled, the supporting infrastructure remains balanced throughout.
Security and reliability features are also embedded within the architecture, which makes the aforementioned flexible configuration possible. By providing robust error handling, AMD can confidently sell partially defective chips as lower-end SKUs without any compromises.
Commercial implications
The commercial implications of AMD’s asymmetric harvesting approach are significant: so far, the company has built a line-up of seven products for desktop PCs and inference servers using just two processors: the Navi 48 and the Navi 44. In theory, AMD could add four or more RDNA 4 GPUs for notebooks to its line-up, if it were interested in competing in that market.
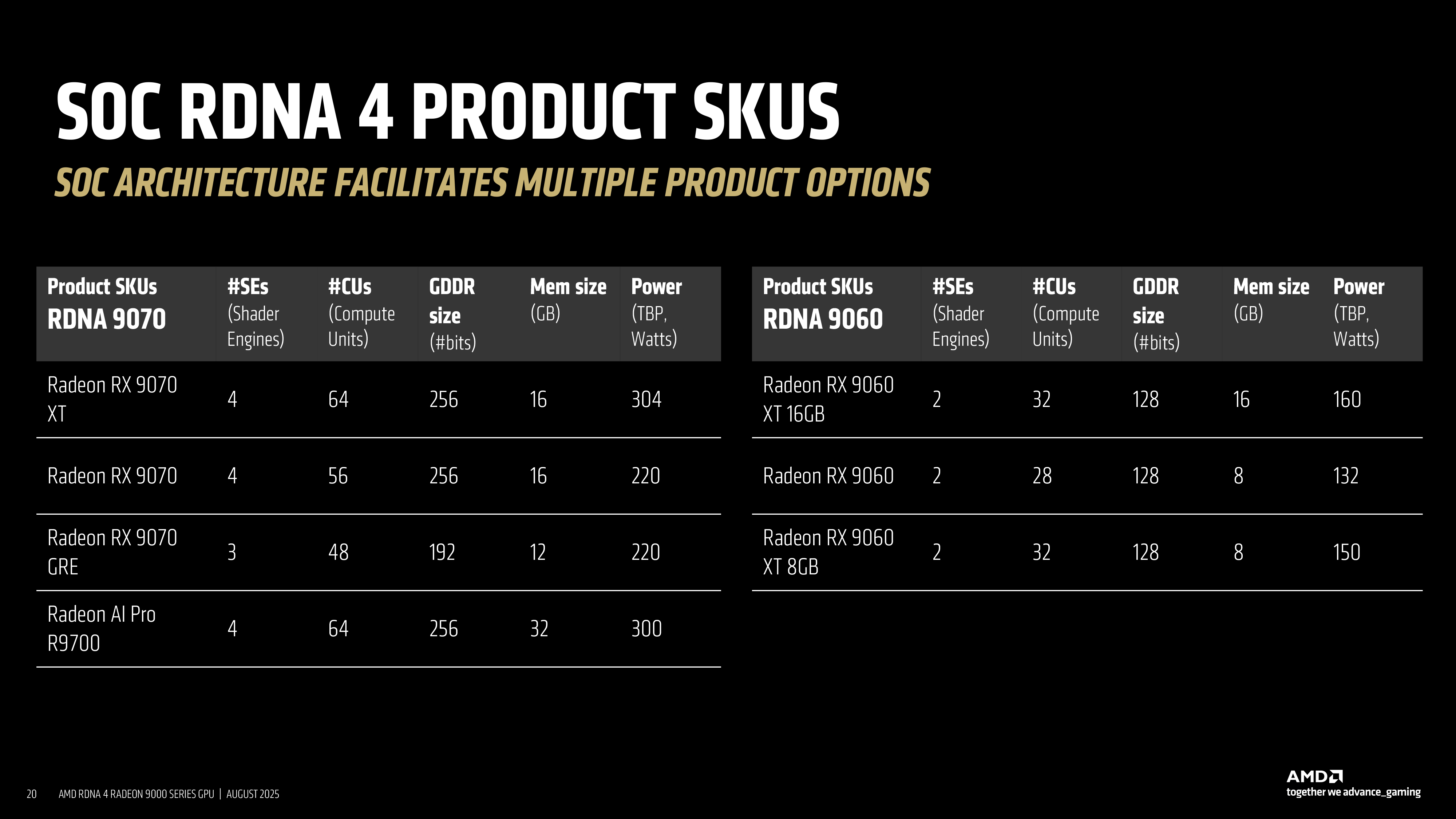
Unfortunately, AMD decided not to pursue the high-end desktop GPU market with its RDNA 4 architecture. If it had developed a high-end RDNA 4-based GPU (by beefing up the command front end and L2 caches and attaching four more SEs, as well as two more memory interfaces), it would have been able to add at least three more products to the line-up and address a lucrative market, which it has seemingly left exclusively to Nvidia.
Nonetheless, asymmetric harvesting assists AMD on both the manufacturing and marketing fronts. By embedding harvesting at multiple levels — from shader engines and work group processors to compute ratios, and memory channels — AMD maximizes output from each wafer, builds products according to market needs, and sustains a consistent feature set across product lines. This makes AMD’s GPUs slightly more lucrative for the company, as it helps keep costs manageable, since it increases the number of dies that can be sold.
AMD’s successful implementation of its asymmetric harvesting capability will offer the company valuable experience for its next generation architecture, named UDNA. How this will impact RDNA 5 and UDNA 6 GPUs is something that remains to be seen, so stay tuned.
Follow Tom’s Hardware on Google News to get our up-to-date news, analysis, and reviews in your feeds. Make sure to click the Follow button.













Leave a Reply